
Enhancing photosynthesis efficiency with an open-source data platform
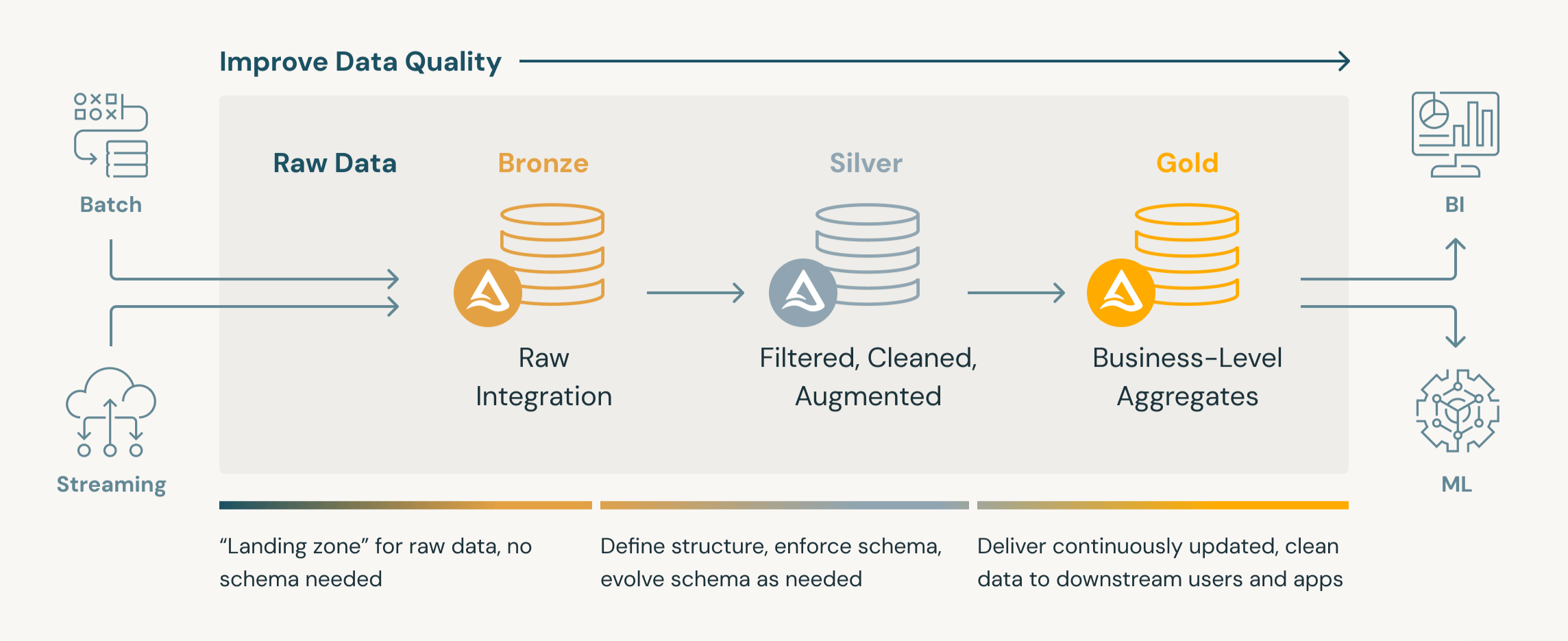
In a world where sustainability and food security are becoming increasingly urgent, improving the efficiency of photosynthesis is key to meaningful innovation. Efficiency of plant photosynthesis is relatively low and in need of large inputs of resources. The Jan Ingenhousz Institute (JII) is conducting pioneering research into photosynthesis. They have developed a sensor that continuously captures real-time data, allowing an improved understanding of photosynthesis in food crops. To unlock the full value of this data for researchers and stakeholders, a data platform is needed that enables both access and integration. Together with JII we are developing an open-science platform based on open-source technologies to foster transparency, collaboration and innovation. Our journey starts with an in-depth exploration of the needs of end users and stakeholders, forming the basis for a strategic vision. This vision becomes the foundation for a proof of concept, paving the way for continuous development and iteration. We are exploring the use of Databricks to ensure scalable, cloud-based data processing and advanced analytic capabilities for researchers. With decades of experience in developing digital products that unite complex technology with human needs, we ensure the data platform is not only technically robust but also genuinely valuable to the scientific community. We achieve this by storing every dataset in a Medallion-style stack. This way, we preserve a complete, time-stamped lineage of how each data point travels from device sensor to published chart. Researchers (and reviewers) can drill down at any point and see: This transparent chain of custody does two things for external validity: By applying this specific architecture, the JII open-science platform enables researchers worldwide to contribute, validate, and reuse data to accelerate the collective scientific progress. Medaillon-style stack architecture sketch. This collaboration reflects our strong belief in driving societal impact through technology. By making science more accessible, efficient, and data-driven, we contribute to a future where innovation and sustainability go hand in hand. INFO’s role: Strategy, Proof of Concept and Product Development
Shaping a future of continuous insight